# Vue2.x 源码概览
前言
简单介绍 vue(v2.7.14) 内部运行原理,模板代码与 options 代码是如何关联起来的
- vue 框架时一个以
MVVM为架构的前端框架- M:代表数据,这里可以简单理解成项目中
data对象数据 - V:代表视图,这里可以简单理解为项目中
template模板 - VM:代表视图模型,是连接数据和视图的桥梁,可以简单理解为数据劫持,
data变化通过视图模型更新到视图上,template变化通过事件监听更新data,然后通过视图模型更新视图
- M:代表数据,这里可以简单理解成项目中
- 代码初次流程结构示意图
`main.js ` | `Vue2.x`
import App from './App.vue' |
1.new Vue({ <-------- | 1._init 3.$mount
render(h) { | | |
return h(<App />); | | |
}, | 1.0.mergeOptions render
2}).$mount("#app"); | | |
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - -| initLifecycle vnode
2<template>{{a}}</template> | | |
<script> | initEvents path
1.0.export default { | | |
1.2.data() { | initRender dom
return { | |
a: '' | 1.1.beforeCreate
} | |
}, | 1.2.initInjections
1.3.props:{ | |
a:{ | 1.3.initState
type:String | |
} | 1.4.initProvide
}, | |
1.4.provide:{ | 1.5.created
b:this |
}, | 2.$mount
1.2.inject:{ | |
b: 'b' | 2.compiler
}, | |
1.1.beforeCreate(){}, | ast
1.5.created(){}, | |
beforeMount(){}, | optimize
mounted(){}, | |
methods:{} | gencode
} |
</script> |
`App.vue` |
|
|
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 1.不同项目
# 1.1 首次加载
通过以下案例来了解 Vue 首次加载的全部过程:
import Vue from "vue"
new Vue({
render(h) {
return h(<App />)
},
}).$mount("#app")
2
3
4
5
6
这里就包含两大部分:
- 实例化 Vue,将相关参数以对象的形式传入到 Vue 内部
- 调用 Vue 实例上的$mount 方法
据此可以将 Vue 看成两个阶段:
- new Vue 阶段
- 1._init:将用户传入的参数进行初始化处理
- $mount 阶段
- 2.$mount: 将 template 模板进行编译生成 render 函数
- 3.mount: 实例化组件 Watch,将 render 转换为 Vnode,将 Vnode 插入到 dom 中
# 1.2 组件更新
# 1.3 组件销毁
# 1.4 异步组件
# 1.5 源码结构
├── compiler # 编译相关
│ ├── codegen # ├── 将编译结果生成render
│ ├── directives # ├── 编译指令
│ ├── parser # ├── 解析template
│ ├── create-compiler.js # ├── 创建编译函数
│ ├── error-detector.js # ├──
│ ├── helpers.js # ├──
│ ├── index.js # ├── 入口文件
│ ├── optimizer.js # ├── 优化编译结果
│ └── to-function.js # └──
├── core # 核心代码
│ ├── components # ├── 组件相关
│ ├── global-api # ├── 全局API
│ ├── instance # ├── 创建Vue实例
│ ├── observer # ├── 响应式
│ ├── util # ├── 工具方法
│ ├── vdom # ├── 虚拟dom
│ ├── config.js # ├──
│ └── index.js # └── 入口文件
├── platforms # 不同平台的支持
│ ├── web # ├── web平台
│ └── weex # └── weex平台
├── server # 服务
│ ├── bundle-renderer # ├──
│ ├── optimizing-compiler # ├──
│ ├── template-renderer # ├──
│ ├── webpack-plugin # ├──
│ ├── create-basic-renderer.js # ├──
│ ├── create-renderer.js # ├── 路由配置文件
│ ├── render-context.js # ├──
│ ├── render-stream.js # ├──
│ ├── render.js # ├── 渲染相关
│ ├── util.js # ├── 工具方法
│ └── write.js # └──
├── sfc # .vue 文件解析
│ └── parser.js # └──
├── shared # 共享代码
│ ├── constants.js # ├── 路由配置文件
│ └── util.js # └── 共享工具方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 1.6 源码运行示意图
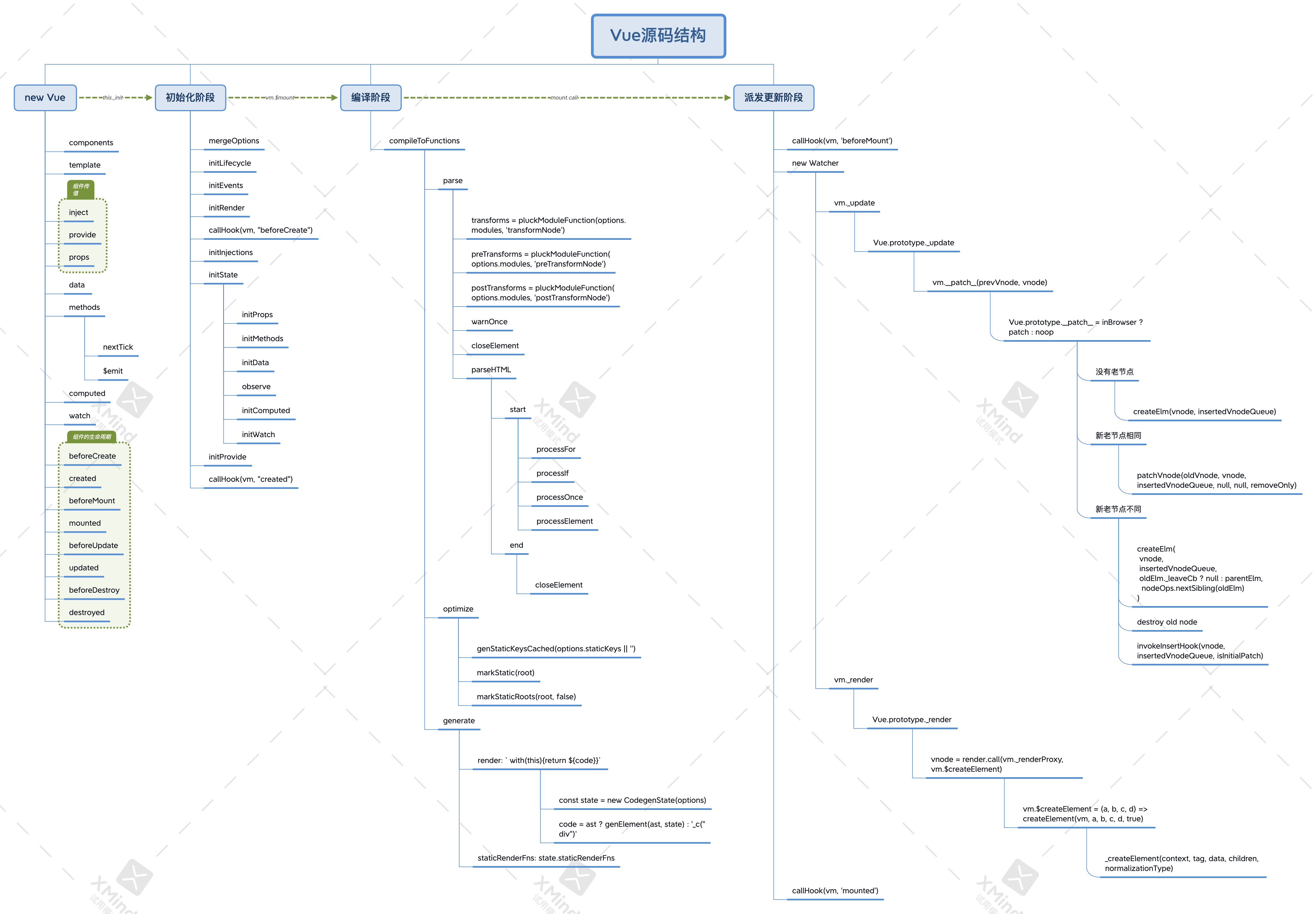
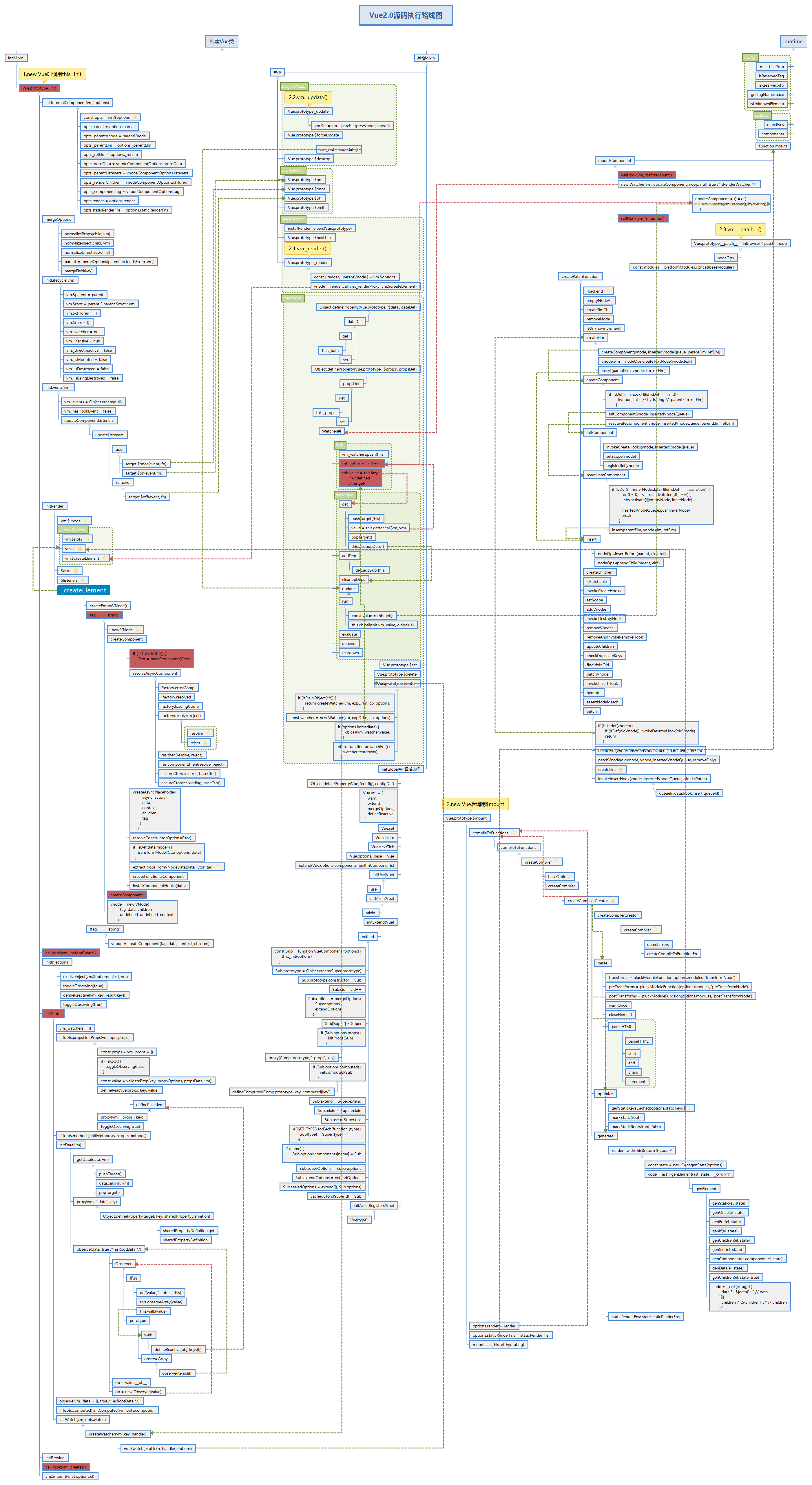
# 1._init 阶段
用户在 new Vue(options)时会将用户的数据传递到 vue 内部做处理。
Vue 会调用 _init 函数进行初始化
function Vue(options) {
this._init(options)
}
2
3
这里的 init 过程,它会合并配置,初始化生命周期、事件、 props、 methods、 data、 computed 与 watch 等。
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm = this
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor), //1.合并配置(如:用户写的生命周期函数)
options || {},
vm
)
initLifecycle(vm) //2.初始化生命周期
initEvents(vm) //3.初始化事件
initRender(vm) //4.初始化渲染函数
callHook(vm, "beforeCreate") //5.使用callHook调用生命周期函数
initInjections(vm) //6.初始化inject
initState(vm) //7.初始化data、props、methods、computed、watch
initProvide(vm) //8.初始化provide
callHook(vm, "created") //9.使用callHook调用生命周期函数
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) //10.挂载到根节点上
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
提示
这里重点要看的是initState,这个方法会处理用户传入的 props、methods、data、computed、watch。
# 1.1 初始化 data 过程
将用户的数据变成响应式数据,为依赖收集和派发更新做准备
function initState(vm) {
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props) //初始化 props
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods) //methods
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm) //初始化 data
} else {
observe((vm._data = {}), true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed) //初始化 computed
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch) //初始化 watch
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
提示
这里重点要看的是initData,Vue 内部数据进入这里会将数据进行响应式处理,以 data 中的数据简单来说,就是将 data 中的对象添加 get 和 set,变成响应式数据,在访问数据时触发 get 时通过 dep 进行依赖收集,在设置数据时通过 set 进行派发更新。
initData:将用户的 data 数据变成响应式数据
- 首先使用 observe 对数据进行观测
function initData(vm) {
var data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === "function" ? getData(data, vm) : data || {}
var keys = Object.keys(data)
observe(data, true)
}
2
3
4
5
6
- 然后实例化观测数据
function observe(value, asRootData) {
var ob
ob = new Observer(value)
return ob
}
2
3
4
5
- 最后给每个对象添加侦听器(dep)
export class Observer {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, "__ob__", this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
walk(obj) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
observeArray(items) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
提示
这里会分别对数组类型的数据和对象类型的数据进行不同的处理,简单的来说对象通过数据劫持,数组通过修改原型上的方法,来拦截相关操作
数组类型
Observer.prototype.observeArray = function observeArray(items) {
for (var i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
2
3
4
5
对象类型
export function defineReactive(obj, key, val, customSetter, shallow) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
},
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
其中最重要的是通过 Object.defineProperty 设置 setter 与 getter 函数,用来实现「响应式」以及「依赖收集」,后面会详细讲到,这里只要有一个印象即可。
# 2.$mount 阶段
前面初始化时我们看到
new Vue({ template: "<div>{{ hi }}</div>" }).$mount("#app")
new Vue 其实走的是初始化的逻辑,当初始化走完了,就是数据都变成响应式数据后,就开始挂载了【$mount】
我们可以看做是编译的起点
Vue.prototype.$mount = function(el, hydrating) {
el = el && query(el)
const options = this.$options
if (!options.render) {
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(
template,
{
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments,
},
this
)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
如果是运行时编译,即不存在 render function 但是存在 template 的情况,需要进行「编译」步骤
compile 编译可以分成
parseoptimizegenerate
三个阶段,最终需要得到 render function。
export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile(
template,
options
) {
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options)
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options)
}
const code = generate(ast, options)
return {
ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns,
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 2.1 parse
parse阶段在 parseHTML 时会用正则等方式循环解析 template 模板中的指令、class、style 等数据,形成 AST。
export function parse(template, options) {
parseHTML(template, {
warn,
expectHTML: options.expectHTML,
isUnaryTag: options.isUnaryTag,
canBeLeftOpenTag: options.canBeLeftOpenTag,
shouldDecodeNewlines: options.shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref: options.shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
shouldKeepComment: options.comments,
start(tag, attrs, unary) {
const ns =
(currentParent && currentParent.ns) || platformGetTagNamespace(tag)
if (isIE && ns === "svg") {
attrs = guardIESVGBug(attrs)
}
let element = createASTElement(tag, attrs, currentParent)
if (ns) {
element.ns = ns
}
processFor(element)
processIf(element)
processOnce(element)
processElement(element, options)
},
end() {
closeElement(element)
},
})
return root
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 2.2 optimize
optimize 的主要作用是标记 static 静态节点,这是 Vue 在编译过程中的一处优化,后面当 update 更新界面时,会有一个 patch 的过程, diff 算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了 patch 的性能。
export function optimize(root, options) {
if (!root) return
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || "")
isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no
markStatic(root)
markStaticRoots(root, false)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 2.3 generate
generate 是将 AST 转化成 render function 字符串的过程,得到结果是 render 的字符串以及 staticRenderFns 字符串。
在经历过 parse、optimize 与 generate 这三个阶段以后,组件中就会存在渲染 VNode 所需的 render function 了。
export function generate(ast, options) {
const state = new CodegenState(options)
const code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")'
return {
render: `with(this){return ${code}}`,
staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns,
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 3.mount 阶段
此阶段分为几个小阶段:
- 3.1 new Watch:将每个组件用 Watch 进行实例化,执行过程中,会将 Watch 实例放到一个类似全局变量上。
- 3.2 _render:执行 render 函数,首先会访问 data 中用户的数据触发 get 方法,配合 Dep 进行依赖的收集,此时之前定义的响应式数据中的 Dep 实例内部的数组中会存储这个 Watch 实例,这样数据和模板就关联起来了,其次生成 Vnode 实例为后续更新 dom 提供参数
- 3.3 _update:将 vnode 通过 path 派发到 dom 上 在$mount 中执行到了最后会以 mount.call 的形式调用之前缓存在 mount 中的方法,进入此代码执行环境
# 3.1 new Watch
首先会通过执行mountComponent进入组件挂载逻辑,依次执行以下比较重要的逻辑
- mountComponent
- callHook(vm, 'beforeMount'):执行生命周期
beforeMount中的事件 - new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, null, true /_isRenderWatcher _/)
- callHook(vm, 'mounted'):执行生命周期
mounted中的事件
- callHook(vm, 'beforeMount'):执行生命周期
其中 new Watcher 是重点, updateComponent 是一个函数
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
2
3
其在实例化过程中:
- 1 this.getter = updateComponent
- 2 this.get(): get 是 Watch 上的一个方法,实例化会自动调用 get
- pushTarget(this):Dep.target=this(也就是 Watch 实例自己),方便在实例化组件 Watch 时,其他地方能拿到这个 Watch 实例,全局有且仅有一个
- this.getter.call(vm, vm):也就是 updateComponent()
- popTarget():Dep.target=null
- this.cleanupDeps():清除 Watch 内部数组存储的 Dep 实例
# 3.2 _render
Watch 实例化过程中 get 中执行 updateComponent,会将 vm._render()执行,然后
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
其中的 render 就是 jsx 语法的 render 函数,继续下去会通过以下几步:
vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true)
创建原生标签 vnode
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
vnode = new VNode(tag, data, children, undefined, undefined, context)
# 3.3 _update
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
const patch = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules })
执行 patch 方法
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
将 Vnode 插入到页面中
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
总结:
页面的初始化阶段几步就是这几步:
首先初始化参数,目的是将普通对象数据转换为响应式数据,这样访问数据会触发 get 方法,修改数据会触发 set 方法,当模板中的数据第一次访问时,在 get 中用变量将这个模板记录下来,下次更新数据触发 set 方法时,可以通知之前记录下来的模板更新数据
然后编译 template,目的是将 template 转换成 render 函数,因为 template 中的语法浏览器是不识别的必须转为通用的语法形式(如:jsx);然后将其传入 Watch 进行实例化,目的是实例化过程中会执行 render 方法,访问 data 中的数据触发 get 方法完成依赖收集,这样 data 和模板就建立联系了
最后将 render 转换成 Vnode,通过 path 方法插入到 dom 中
简单实现 Vue 类
- 1.拿到 vm 中的属性和 data 里面的值
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
//this.$el $data $options
this.$el = options.el
this.$data = options.data
let computed = options.computed
let methods = options.methods
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 2.把 template 中的值用 data 中的数据替换
class Compiler {
constructor(el, vm) {
this.el = this.isElementNode(el) ? el : document.querySelector(el)
this.vm = vm
let fragment = this.node2fragment(this.el)
this.compile(fragment)
this.el.appendChild(fragment)
}
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith("v-")
}
compileElement(node) {
let attributes = node.attributes
;[...attributes].forEach((attr) => {
let { name, value: expr } = attr
if (this.isDirective(name)) {
let [, directive] = name.split("-")
let [directiveName, eventName] = directive.split(":")
CompileUtil[directiveName](node, expr, this.vm, eventName)
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
let content = node.textContent
if (/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/.test(content)) {
CompileUtil["text"](node, content, this.vm)
}
}
compile(node) {
let childNodes = node.childNodes
;[...childNodes].forEach((child) => {
if (this.isElementNode(child)) {
this.compileElement(child)
this.compile(child)
} else {
this.compileText(child)
}
})
}
node2fragment(node) {
let fragment = document.createDocumentFragment()
let firstChild
while ((firstChild = node.firstChild)) {
fragment.appendChild(firstChild)
}
return fragment
}
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}
CompileUtil = {
getVal(vm, expr) {
return expr.split(".").reduce((data, current) => {
return data[current]
}, vm.$data)
},
setValue(vm, expr, value) {
expr.split(".").reduce((data, current, index, arr) => {
if (index == Array.length - 1) {
return (data[current] = value)
}
return data[current]
}, vm.$data)
},
model(node, expr, vm) {
let fn = this.updater["modelUpdater"]
node.addEventListener("input", (e) => {
let value = e.target.value
this.setValue(vm, expr, value)
})
let value = this.getVal(vm, expr)
fn(node, value)
},
html(node, expr, vm) {},
on(node, expr, vm, eventName) {},
text(node, expr, vm) {
let fn = this.updater["textUpdater"]
let content = expr.replace(/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g, (...args) => {
return this.getVal(vm, args[1])
})
fn(node, content)
},
updater: {
modelUpdater(node, value) {
node.value = value
},
htmlUpdater(node, value) {
node.innerHTML = value
},
textUpdater(node, value) {
node.textContent = value
},
},
}
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$el = options.el
this.$data = options.data
let computed = options.computed
let methods = options.methods
if (this.$el) {
new Compiler(this.$el, this)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
- 3.数据劫持,监听
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subs = []
}
addSub(watcher) {
this.subs.push(watcher)
}
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(watcher => watcher.update())
}
}
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, expr, cb) {
this.vm = vm
this.expr = expr
this.cb = cb
this.oldValue = this.get()
}
get() {
Dep.target = this
let value = CompileUtil.getVal(this.vm, this.expr)
Dep.target = null
return value
}
update() {
let newVal = CompileUtil.getVal(this.vm, this.expr)
if (newVal !== this.oldValue) {
this.cb(newVal)
}
}
}
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.observer(data)
}
observer(data) {
if (data && typeof data == 'object') {
for (let key in data) {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
}
}
}
defineReactive(obj, key, value) {
this.observer(value)
let dep = new Dep()
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
return value
},
set: newVal => {
if (newVal != value) {
this.observer(newVal)
value = newVal
dep.notify()
}
}
})
}
}
class Compiler {
constructor(el, vm) {
this.el = this.isElementNode(el) ? el : document.querySelector(el)
this.vm = vm
let fragment = this.node2fragment(this.el)
this.compile(fragment)
this.el.appendChild(fragment)
}
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith("v-")
}
compileElement(node) {
let attributes = node.attributes;
[...attributes].forEach(attr => {
let {
name,
value: expr
} = attr;
if (this.isDirective(name)) {
let [, directive] = name.split("-")
let [directiveName, eventName] = directive.split(":")
CompileUtil[directiveName](node, expr, this.vm, eventName)
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
let content = node.textContent;
if (/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/.test(content)) {
CompileUtil["text"](node, content, this.vm)
}
}
compile(node) {
let childNodes = node.childNodes;
[...childNodes].forEach(child => {
if (this.isElementNode(child)) {
this.compileElement(child)
this.compile(child)
} else {
this.compileText(child)
}
})
}
node2fragment(node) {
let fragment = document.createDocumentFragment()
let firstChild
while (firstChild = node.firstChild) {
fragment.appendChild(firstChild)
}
return fragment
}
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}
CompileUtil = {
getVal(vm, expr) {
return expr.split(".").reduce((data, current) => {
return data[current]
}, vm.$data)
},
setValue(vm, expr, value) {
expr.split(".").reduce((data, current, index, arr) => {
if (index == arr.length - 1) {
return (data[current] = value)
}
return data[current]
}, vm.$data)
},
model(node, expr, vm) {
let fn = this.updater["modelUpdater"]
new Watcher(vm, expr, newVal => {
fn(node, newVal)
})
node.addEventListener('input', e => {
let value = e.target.value
this.setValue(vm, expr, value)
})
let value = this.getVal(vm, expr)
fn(node, value)
},
html(node, expr, vm) {
let fn = this.updater["htmlUpdater"]
new Watcher(vm, expr, newVal => {
fn(node, newVal)
})
let value = this.getVal(vm, expr)
fn(node, value)
},
getContentValue(vm, expr) {
expr.replace(/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g, (...args) => {
return this.getVal(vm, args[1])
})
},
on(node, expr, vm, eventName) {
node.addEventListener(eventName, e => {
vm[expr].call(vm, e)
})
},
text(node, expr, vm) {
let fn = this.updater["textUpdater"]
let content = expr.replace(/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g, (...args) => {
new Watcher(vm, args[1], () => {
fn(node, this.getContentValue(vm, expr))
})
return this.getVal(vm, args[1])
})
fn(node, content)
},
updater: {
modelUpdater(node, value) {
node.value = value
},
htmlUpdater(node, value) {
node.innerHTML = value
},
textUpdater(node, value) {
node.textContent = value
}
}
}
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$el = options.el
this.$data = options.data
let computed = options.computed
let methods = options.methods
if (this.$el) {
new Observer(this.$data)
for (let key in computed) {
Object.defineProperty(this.$data, key, {
get: () => {
return computed[key].call(this)
}
})
}
for (let key in methods) {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
return methods[key]
}
})
}
this.proxyVm(this.$data)
new Compiler(this.$el, this)
}
}
proxyVm(data) {
for (let key in data) {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
return data[key]
},
set(newVal) {
data[key] = newVal
}
})
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
项目代码 →