# 十.桥接模式
- 将抽象部分与他的实现部分分离,这样抽象化与实现化解耦,使他们可以独立的变化
- 应用场景是实现系统可能有多个角度分类,每一种角度都可能变化
- 桥方可以通过实现桥接口进行单方面扩展,而另一方可以继承抽象类而单方面扩展,而之间的调用就从桥接口来作为突破口,不会受到双方扩展的任何影响
# 1.类图
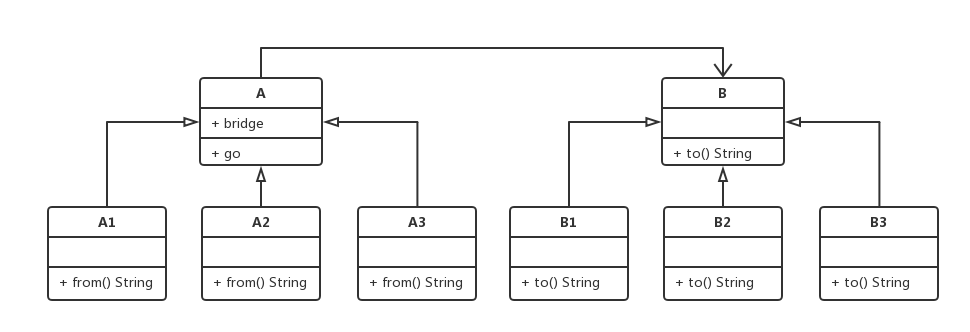
# 2.代码
class A {
constructor(bridge) {
this.position = "A地点"
this.bridge = bridge
}
go() {
console.log(`从${this.from()}到达${this.bridge.to}`)
}
from() {
throw new Error("子类必须实现此方法")
}
}
class A1 extends A {
from() {
return "A1"
}
}
class A2 extends A {
from() {
return "A2"
}
}
class B {
to() {
throw new Error("子类必须实现此方法")
}
}
class B1 extends B {
to() {
return "B1"
}
}
class B2 extends B {
to() {
return "B2"
}
}
let b1 = new B2()
let b2 = new B()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.16.4"
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
let express = require("express")
let app = express()
let path = require("path")
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
console.log(__dirname)
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "2.html"))
})
app.get("/user/:id", (req, res) => {
let id = req.params.id
res.json({
id,
name: id,
})
})
app.listen(8080, () => {
console.log(8080)
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
canvas {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="1000" height="600"></canvas>
<script>
function Position(x, y) {
this.x = x
this.y = y
}
function CircleColor(color) {
this.color = color
}
function Circle(x, y) {
this.position = new Position(x, y)
this.CircleColor = new CircleColor(CircleColor)
}
Circle.prototype.render = function () {
let canvas = document.getElementById("canvas")
let ctx = canvas.getContext("2d")
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.arc(this.position.x, this.position.y, 100, 0, 2 * Math.PI)
ctx.fillStyle = this.CircleColor.color
ctx.fill()
}
let c = new Circle(200, 200, 200, "red")
c.render()
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li data-id="1">用户1</li>
<li data-id="2">用户2</li>
</ul>
<p id="content"></p>
<script>
let lis = document.querySelectorAll("li")
for (let i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {
lis[i].addEventListener("click", getUserById)
}
function getUserById(event) {
let id = event.target.dataset.id
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("GET", `/user/${id}`, true)
xhr.responseType = "json"
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
let user = xhr.response
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = user.name
}
}
xhr.send()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36